

|

|
|
home | sitemap | abstract | introduction | chaos | thinking | checklist | migrating | recovery pushpull | cost | career | workshop | isconf | list_and_community | papers | references |
Checklist
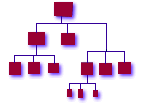
A certain sequence of events needs to occur while creating an enterprise cluster infrastructure. Most of these events are dependent on earlier events in the sequence. Mistakes in the sequence can cause non-obvious problems, and delaying an event usually causes a great deal of extra work to compensate for the missing functionality. These relationships are often not readily apparent in the "heat of the moment" of a rollout. We found that keeping this sequence in mind was invaluable whether creating a new infrastructure from vanilla machines fresh out of the box, or migrating existing machines already in place into a more coherent infrastructure. If you are creating a new infrastructure from scratch and do not have to migrate existing machines into it, then you can pretty much follow the bootstrap sequence as outlined below. If you have existing machines which need to be migrated, see Migrating From an Existing Infrastructure . As mentioned earlier, the following model was developed during the course of four years of mission-critical rollouts and administration of global financial trading floors. The typical infrastructure size was 300-1000 machines, totaling about 15,000 hosts. Nothing precludes you from using this model in much smaller environments -- we've used it for as few as three machines. This list was our bible and roadmap -- while incomplete and possibly not in optimum order, it serves its purpose. See Figure 1 for an idea of how these steps fit together. 
The following sections describe these steps in more detail.
Figure 1 - Infrastructure Bootstrap Sequence |
|
||||||||
|
© Copyright 1994-2007 Steve
Traugott,
Joel Huddleston,
Joyce Cao Traugott
In partnership with TerraLuna, LLC and CD International |
||||||||